로지스틱 회기란, 참 거짓을 판명하는 ox기계라고 보면 된다. 오로지 1(정답)과 0(오답)뿐이다.
그러한 참 거짓을 나타내는 그래프는 다음과 같고, 이를 시그모이드 함수라고 한다.
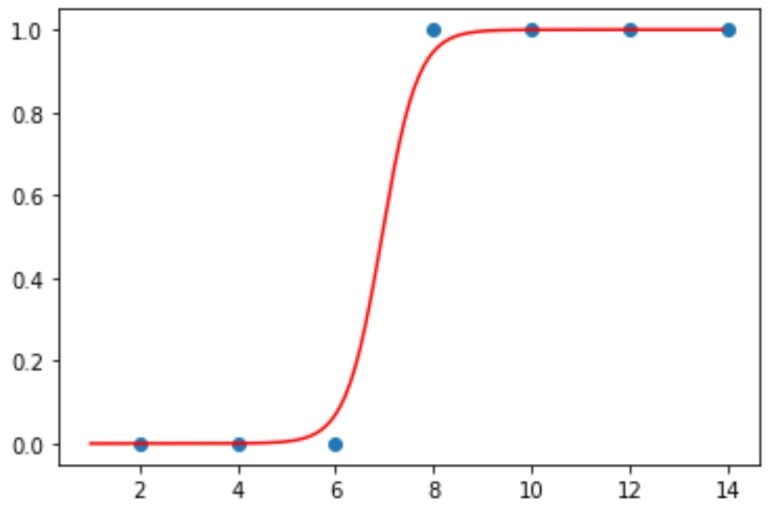
시그모이드 함수 (Sigmoid function)
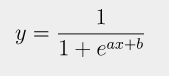
오차공식 = 로그함수
다중 로지스틱 회기 코드
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 실행할 때마다 같은 결과를 출력하기 위한 seed 값 설정
seed = 0
np.random.seed(seed)
tf.set_random_seed(seed)
# x,y의 데이터 값
x_data = np.array([[2, 3],[4, 3],[6, 4],[8, 6],[10, 7],[12, 8],[14, 9]])
y_data = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,1]).reshape(7, 1)
# 입력 값을 플래이스 홀더에 저장
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, shape=[None, 2])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, shape=[None, 1])
# 기울기 a와 bias b의 값을 임의로 정함.
a = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([2,1], dtype=tf.float64)) # [2,1] 의미: 들어오는 값은 2개, 나가는 값은 1개
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], dtype=tf.float64))
# y 시그모이드 함수의 방정식을 세움
y = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, a) + b)
# 오차를 구하는 함수
loss = -tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(y) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - y))
# 학습률 값
learning_rate=0.1
# 오차를 최소로 하는 값 찾기
gradient_decent = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
predicted = tf.cast(y > 0.5, dtype=tf.float64)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype=tf.float64))
# 학습
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(3001):
a_, b_, loss_, _ = sess.run([a, b, loss, gradient_decent], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if (i + 1) % 300 == 0:
print("step=%d, a1=%.4f, a2=%.4f, b=%.4f, loss=%.4f" % (i + 1, a_[0], a_[1], b_, loss_))
# 어떻게 활용하는가
new_x = np.array([7, 6.]).reshape(1, 2) #[7, 6]은 각각 공부 시간과 과외 수업수.
new_y = sess.run(y, feed_dict={X: new_x})
print("공부 시간: %d, 개인 과외 수: %d" % (new_x[:,0], new_x[:,1]))
print("합격 가능성: %6.2f %%" % (new_y*100))'Machine Learning > 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [딥러닝] keras 라이브러리 이용해서 모델 설계하기 (0) | 2022.03.13 |
|---|---|
| [모두의 딥러닝] 퍼셉트론, 신경망의 시작 (0) | 2022.03.11 |
| [모두의 딥러닝] 선형회기 (Linear Regression) (0) | 2022.03.11 |
| [모두의 딥러닝] 아나콘다, 텐서플로 설치하고 파이참 연결하기 (0) | 2022.03.11 |
